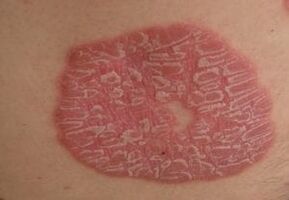
As can be seen, in most patients, psoriasis does not go away on its own, but progresses and becomes more widespread, spreading over the skin.
But with timely diagnosis, treatment is easier and recovery is much faster.
The main thing here is to pay attention to the first signs of psoriasis in time and see a dermatologist immediately.
Characteristics of psoriasis
Early psoriasis may appear as small, red, scaly patches.
The location of such rashes directly depends on the form of the disease.
In most cases, the following can be seen:
- on elbows and knees; at the head of
- (in the hairy area);
- on palms and feet; In the area of wrinkles
- (hips, armpits, areas under the breasts in women).
The size of the initial eruptions (papules) is very small: no more than 4 millimeters in diameter.
However, as the disease progresses, they grow together and form plaques that do not have a clear shape.
Often the appearance of papules is not accompanied by pain and itching. The feeling of discomfort increases with the development of psoriasis and the increase in the size of the affected skin areas.
Pain and itching begin in the affected area and there is a strong burning sensation.
These psoriasis symptoms are complemented by emotional disturbances that can significantly increase the rate of disease spread.
When such rashes are detected, it is inappropriate to start self-medication, because psoriasis in the early stages of development has similarities with other skin diseases.
Therefore, the wrong drugs will not lead to positive results, but will only worsen the situation.
Cumulative Symptoms
Paid lichen belongs to the category of systemic pathologies.
This means that it can affect not only the skin and nails, but also the spine, joints and tendons, as well as certain body systems (eg, endocrine, immune and nervous).
There have been cases where the disease affects the digestive (liver) and urinary (kidney) systems.
The first symptoms of psoriasis
- constant tiredness;
- weakness;
- depressive condition (before depression).
Due to the complex effect of the disease on the body, experts consider it expedient to call it psoriatic disease.
However, the main features of the disease are based on skin damage.
As mentioned above, the first call to the beginning of the development of pathology are small papules in the color range between pale pink and red.
They differ in the symmetrical position on the surface of the skin (wrinkles, back, scalp covered with hair), sometimes in the mucous membrane of the external genitalia.
In the later stages of the disease, the size of the papules may be more than 10 centimeters.
Psoriatic eruptions, depending on their characteristics, are divided into:
- dotted (dimensions are not larger than the beginning of a pin);
- in the form of tears (shape similar to tears, the size of a lentil);
- in the form of a coin (5 mm diameter plates, rounded edges);
- Rarely looks like an arc, ring or map.
On top of the papules, they are covered with scaly plaques formed by keratinized cells of the epidermis and removed without much effort. Initially, they appear in the center of the board and gradually spread further.
Keratin cells contain air cavities, which results in vision and a clear shadow.
Sometimes the elements are surrounded by a pink ring that acts as a plaque growth and an area of inflammation. In this case, the condition of the surrounding skin does not change.
Removal of the plaque reveals a bright, deep red surface based on capillaries, which in turn has very thin walls.
The presence of such small-diameter vessels is due to damage to the structure of the upper layers of the skin, which is disrupted due to the maturation of epidermal cells (keratinocytes), which makes it impossible to distinguish them properly.Symptoms of various forms of psoriasis
Common psoriasis has very specific symptoms, so it is easy to diagnose.
Looks like scaly, round areas that protrude from normal skin and are pink or red in color.
Sometimes in the early stages of the disease there are no typical plaques: small papules may be observed on the scalp and joints (ankles, elbows and knees) before they appear.
They can last long enough and do not cause any discomfort to the patient: nothing itches and does not hurt or does not hurt at all or is practically not felt, it is almost impossible to feel the papules themselves.
They do not wrinkle, but with a small spoon the scales are immediately visible. Such pink seals may disappear in summer or be significantly reduced in size because sunlight affects the skin.
The acute form of psoriasis manifests itself in the form of numerous persistent itchy rashes of brightly colored papules and is the result of the influence of factors that activate the disease.
In order not to confuse it with an allergic reaction, it is necessary to scratch the surface of the board a little before the characteristic phenomena appear.
Seborrheic psoriasis begins on the scalp (hairy area) and then spreads to the face and shoulders.
It is characterized by severe peeling of the skin of the affected area, which is considered by most patients as dandruff, so they do not rush to consult a dermatologist.
This fact allows the disease to progress slowly when the areas behind the forehead and ears are peeled off. And only then do the boards appear.
Psoriatic disease is characterized by damage to the wrinkles of the skin (armpits, genitals and groin, under the breasts in women) mixed with the usual irritation caused by friction or sweat.
This type of disease is characterized by smooth plaques resembling spots. Peeling is not observed, but often moisturized. The spills themselves are bright red, even and bright.
In the case of genital damage, the characteristic symptoms of psoriasis can be misinterpreted as balanoposthitis in men (damage to the head of the penis, as well as the sponge skin on the inside) and vulvitis in women (rashes localized in the labia minora).
The palmar-plantar form of the disease manifests itself in the form of compressed areas resembling calluses covered with yellow scales, the surface of which is difficult to remove.
The affected area is cracked and painful. With this form of the disease, shaving is difficult to cause the appearance of a terminal film and bloody shoulder.
Psoriasis of the nails begins with psoriatic onychodystrophy, one of the first symptoms of this form of the disease, which manifests itself long before the rash.
In the early stages, the edge of the nail is covered with grooves and small depressions.
As the disease progresses, they spread to the root, after which changes in color are observed. The nail freezes and thickens. The manifestations of the disease increase due to circulatory failures.
Epidermal cells accumulate under the nail plate and are bordered on each side by red tissue, which can then peel off after a while.
This type of psoriasis is dangerous because it increases the sensitivity of the tissues, which increases the likelihood of infection. This disease is often mistaken for a fungus.
The moving joints (joints) of the bones are often affected. It is deformed, the joint capsule undergoes dystrophic changes.
Psoriatic arthritis begins with an increase in joint volume accompanied by pain.
The fingers and toes of both hands and feet are the most susceptible to this type of psoriasis.
In severe forms, the disease affects the shoulders and elbows, hips and knees, as well as some parts of the spine.
Effect of psoriasis stages on symptoms
The symptoms of psoriasis are proportional to the season and the stage of the disease.
Often in the spring and summer there is a significant decrease in the activity of the disease, which is facilitated by ultraviolet rays.
Therefore, due to the lack of sun in the autumn-winter period, the disease spreads rapidly. Patients with spring exacerbations are practically absent.
Psoriasis has three stages:
- progressive- persistent appearance of new rashes, characterized by an increase in the size of previously formed plaques and their surroundings with a pink border, the affected area is very itchy and peeling;
- stationary- new debris is no longer visible and old ones do not grow; the top layer of skin in the area of the plaque wrinkles;
- regressive- the skin does not peel, the plaque disappears and leaves high pigmented areas.
Psoriasis Diagnostics
The diagnosis of psoriasis is made on the basis of information obtained from a medical examination of a patient, as well as the symptoms of this or that form of the disease.
The sooner a disease is detected, the faster the treatment process begins. Therefore, more material results will be obtained.
Depending on the nature of the disease, the diagnosis of psoriasis may be limited to a simple examination by a dermatologist.
However, in some cases, if the disease does not manifest itself in any way or does not appear characteristic, problems may arise due to the latency or absence of symptoms. This situation necessitates additional research procedures.
To diagnose, a specific method is used, which consists of gradually shaving the papules along the layer.
As a result of such manipulation, it is possible to distinguish psoriasis from other diseases and identify the characteristic symptoms (psoriatic triad) to make a final diagnosis:
- stearin stain;
- terminal film (pink epidermal cells);
- blood clot (blood droplets appear on the surface of the plaque due to rupture of capillaries).
If necessary, the patient is examined in the form of samples of affected tissues.
X-rays are taken if psoriasis-related arthritis is suspected.
If psoriasis is at an early stage, the diagnosis is not difficult: the picture of osteoporosis is clear.
Subsequent periods include narrowing of the joint space, erosion of bone-forming tissues, osteosclerosis, and periostitis.
If the disease is severe, the wrist and metatarsal joints are destroyed, resulting in complete loss of joint mobility.
It should be noted that all tests are necessary not only for the final diagnosis, but also for differentiation from other diseases that are the same at first glance.
These diseases include: parapsoriasis, seborrheic eczema, lichen rosacea, atopic dermatitis, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.























